

Fish and shellfish are among the healthiest foods on the planet. Seafood is an excellent source of protein and also contains some key nutrients that many people are lacking, such as iodine, selenium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients are actually hard to acquire from any other food source! You can obtain the minimal nutritional benefits of seafood by eating two servings per week, but I suggest eating fish as often as possible.
The majority of the benefits of eating seafood are owed to the essential fats they contain. These are polyunsaturated fats (PUFA) known as omega-3 fatty acids. The human body doesn't manufacture these fats, which means you have to eat seafood or take a supplement. The two types of omega-3 fats found in fish are DHA and EPA. DHA is an essential structural and developmental component of the brain and cell membranes, while EPA has impressive anti-inflammatory benefits as well as showing positive effects on behavior and mood. Both of these fats are great for overall health and have been shown to promote better function of the heart, brain, eyes, and joints.
What are some of the risks of a diet without fish?
There is another type of PUFA called omega-6 fatty acids which do not have the same health benefits. Omega-3s have a strong anti-inflammatory effect in the body, while omega-6 fats are inflammatory. Inflammatory states are a common link throughout most illness and diseases such as depression, obesity, autoimmunity, diabetes, arthritis, chronic fatigue, cancer, neurological disease, and heart disease. To keep inflammation to a minimum, it is important to achieve a good balance between these two fats.
Research shows that our ancestors thrived on a diet that contained a ratio of 1:1 omega-6 to omega-3, while modern diets give us a ratio between 10:1 to 25:1. Most of this omega-6 is coming from the use of vegetable oils and margarine, as well as consuming foods fried in vegetable oil or processed foods made with these fats. These inflammatory fats are also obtained by eating conventionally raised livestock and poultry. The fatty acid profile of these animals has been altered by feeding them an unnatural diet of cereal grains.
The more omega-3 you consume, the less omega-6 is available to promote inflammation in tissues. The pain relief of OTC and prescription NSAIDS can be achieved by simply limiting your consumption of omega-6 fats and eating more fish.
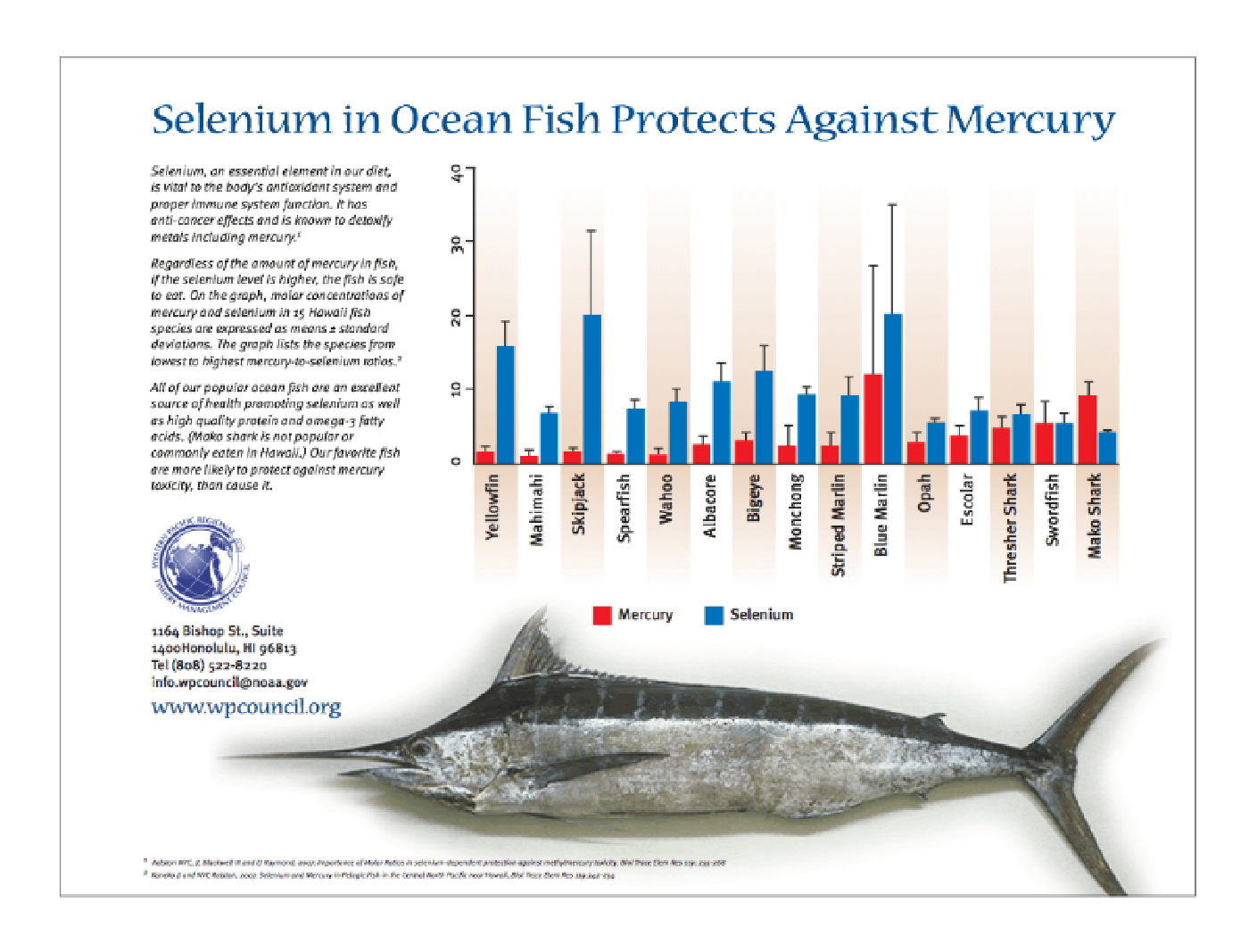
Many people avoid fish because they're worried about high mercury levels. It's true that industrial pollution has caused pervasive bio-accumulation of mercury throughout the seafood chain. The higher you go in the marine food chain, the higher the levels of mercury, so the best way to limit exposure is to avoid larger predatory fish. The fish showing the highest levels of accumulation are shark, whale, tilefish, king mackerel, swordfish, and tuna. Fortunately, the most commonly consumed seafood are the ones with the lowest mercury content, such as salmon, oysters, shrimp, clams, tilapia, and sardines. Another important point to make about mercury is that it cannot be absorbed into any body tissues once it has been bound to selenium. Luckily the most commonly consumed types of seafood are also the highest in selenium.
Let's take a look at some of the best reasons to get more fish in your diet.
Heart Health
The effects of fish oil and seafood on heart disease risk has been studied for decades. One of the most striking findings of these studies is that the benefits from fish oil are not the same as the benefits of regular seafood consumption. Omega-3 supplements such as fish oil have not been consistently proven to offer protection against heart disease. This may be due to the change in molecular activity from the processing of fish oil. The EPA and DHA found in fish remain in their active states unlike the fats found in fish oil, giving fish a more potent effect on the body.
Several observational studies of populations in Japan, Alaska, Finland, and the Netherlands all show a remarkably lower mortality rate among those who ate fish rich in omega-3s several days a week. The same benefits are not seen when eating lean fish such as tilapia or cod. Studies also show reductions in total triglyceride levels and an increase in HDL cholesterol. Also, DHA has been shown to change the size of the dangerous small, dense LDL cholesterol particles to the large, fluffy LDL particles which lower the risk of cardiovascular disease.

Sign up for the weekly newsletter to receive expert tips on fitness and nutrition.
Brain Health
Studies show that regular consumption of fish boosts brain health in several ways. The brain contains very high concentrations of DHA, especially in the regions related to memory, emotion, and learning. The brain is structurally dependent on DHA. DHA enhances the growth of new brain cells and improves the ability of brain cells to communicate. Supplementation with fish oil has been shown to increase overall brain volume and protect the brain from age-related shrinkage. DHA has also been shown to increase the amounts of grey matter in the brain. Grey matter is the highly-active, thinking part of the brain that processes information. Deficits in grey matter volume have been linked to behavioral disorders, alcoholism, pathological lying, and low IQ. Low levels of DHA in the brain have been strongly linked to increased risk for Alzheimer's, strokes, learning disabilities, and psychiatric disorders.
If your brain tissue has a high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, you can expect high levels of brain inflammation due to the decreased levels of EPA. EPA is the lipid that protects against inflammation by competing with omega-6 fats. Chronic brain inflammation leads to poor cognitive function, and eventually, degeneration. Two of the most prevalent conditions in the developed world, obesity and depression, are both linked to chronic brain inflammation. Both regular fish intake and fish oil supplementation have been shown to lower inflammation, improve brain function and reverse age-related deterioration.
Mood Disorders and Stress
Omega-3 fatty acids may play an important role in psychiatric and mood disorders such as depression. Research has shown that depression and hostility are more common in individuals with low levels of omega-3 fatty acids. A higher consumption of fish has been shown in many studies to reduce symptoms of depression, especially in women. Not surprisingly, the highest rates of depression are reported in countries with the lowest rates of fish consumption.
The omega-3 depletion commonly seen in mood disorders may also be related to stress. Stress causes inflammation in the brain which is handled by EPA. If the stress is repeated and chronic, omega-3 stores could be quickly sapped. Without a constant source of these fats in the diet, the brain will remain in this inflamed state. Most improvements in behavioral and affective disorders have been shown using higher dosages of EPA. Improvements have been observed in ADD, aggression, autism, depression, PMS, and bipolar disorder.
Dopamine levels are also drained when you're experiencing repeated stress. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter linked to energy, memory, drive, and pleasure. Eating foods rich in the amino acid tyrosine (like seafood) will increase dopamine levels, which may be why populations with heavy fish consumption report feeling less stressed. One study has shown that an increase in tissue omega-3 levels was associated with a boost in dopamine levels in the frontal cortex of the brain. Increased dopamine results in an overall better mood and motivation.
Simply by eating fish a few times a week, you can improve your brain function, protect your heart, and improve your mood! So which fish should you be eating to gain these benefits? Since omega-3 fatty acids are the key nutrient, stick to fatty cold-water fish like salmon, trout, herring, sardines, anchovies, halibut, and light tuna. Wild-caught fish are best since they have access to their natural diet that includes algae rich in omega-3 fats. Farm raised fish usually have only HALF the amount of omega-3s and their feed is from conventionally grown crops sprayed with herbicides and pesticides. Still, eating farmed fish is better than eating no fish. Other excellent seafood options include oysters, mussels, clams, crabs, and lobster. Try to include seafood in your diet at least twice a week to start reaping the benefits!
FACEBOOK COMMENTS WILL BE SHOWN ONLY WHEN YOUR SITE IS ONLINE